Product Name
Waste gas treatment in the printing and coating industry
Product Description
Product Name
The printing and coating industry is a key area for industrial volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter pollution. Its waste gas is characterized by complex composition, flammability and explosiveness, and high treatment difficulty. The following is a systematic analysis from aspects such as waste gas characteristics, treatment technologies, typical processes, and policy trends, and targeted solutions are provided:
I Core Characteristics of Industry Waste Gas
(1) Waste Gas from the Printing Industry Source: Ink preparation, printing process (offset printing, gravure printing, flexographic printing), drying / laminating process, equipment cleaning. Composition: VOCs: Toluene, xylene, ethyl acetate, ethanol, methyl ethyl ketone, isopropyl alcohol, etc. (solvent – based inks have a high proportion). Particulate Matter: Ink particles, paper fiber dust (more obvious in letterpress printing).
(2) Exhaust Gas from the Painting Industry Source: Spraying (atomization of paint and coating), leveling (solvent evaporation), drying (high-temperature evaporation), pre-treatment (degreasing and volatilization).
Composition: VOCs: Xylene, butyl acetate, methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK), cyclohexanone, styrene, etc. Particulate Matter: Paint mist (resin and pigment particles, particle size 1 – 100μm), grinding dust. Other Pollutants: Some contain cyanides (electrophoresis process), heavy metals (such as chromates).
Features: The waste gas in the spraying workshop has high humidity and contains viscous paint mist, which can easily clog the treatment equipment; The waste gas from drying has high temperature and high concentration (the VOCs concentration can reach 2000 – 5000mg/m³), and has a high risk of explosion and fire.
II. Core Processing Technologies and Application Scenarios
▌Pretreatment technology: Removal of particulate matter and viscous pollutants
| Technology, | principle | application scenario | key parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water curtain / Water cyclone defogging | The water curtain captures paint mist particles, forming wastewater. | Pre – treatment at the front – end of automotive spraying and furniture painting lines | The paint mist removal rate is > 90%, and wastewater treatment facilities need to be provided. |
| Dry filtration | Fiberglass wool / non-woven fabric intercepts particulate matter | Printing and drying line, hardware spraying line | The filtration efficiency is > 95% and the pressure drop is < 500 Pa. |
| Electrostatic demisting | The high – voltage electric field adsorbs charged particles | High-concentration paint mist scenarios (such as coil coating) | Low energy consumption, and the processed air volume can reach 100,000 m³/h |
▌VOCs Treatment Technologies: Selection Based on Concentration Levels
(1) Low-concentration waste gas (<1000mg/m³)
| technology | Principle | Typical process | Applicable scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
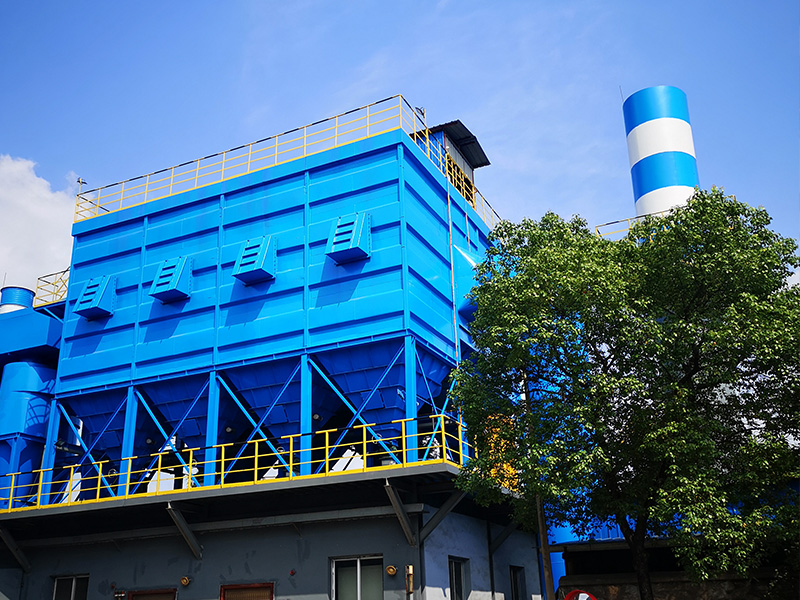
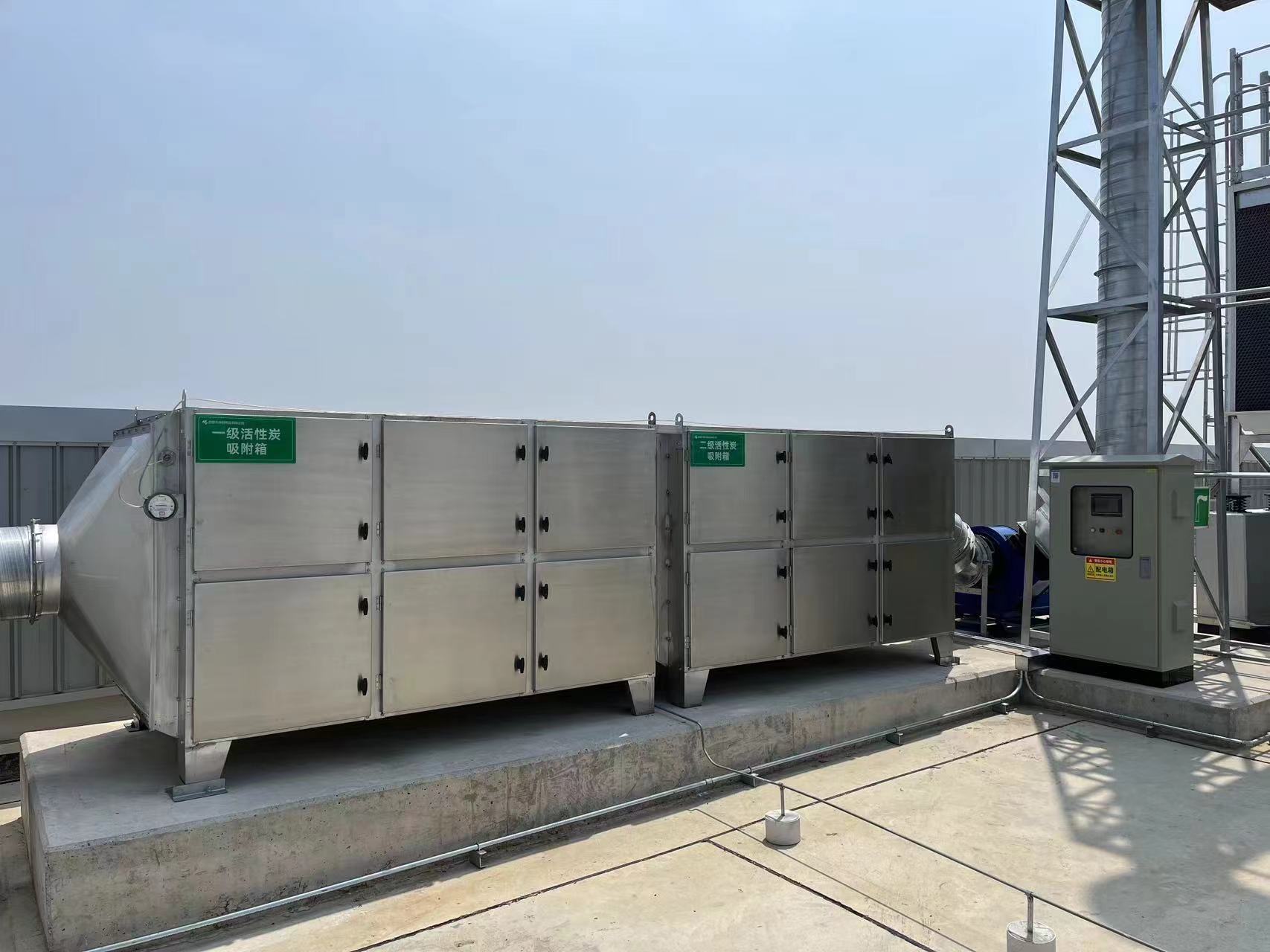
| Activated carbon adsorption | Microporous adsorption of VOCs, regeneration or replacement after saturation | Activated carbon box + fan | Small and medium-sized printing workshops, furniture touch-up paint rooms |
| Biological treatment | Microbial degradation of water – soluble VOCs | Biological filter / biological trickling filter tower | Water – based ink printing, food packaging printing |
| Photocatalytic oxidation | UV light + catalyst decomposition of VOCs | Photo – oxygen catalytic equipment + activated carbon | Laboratory spraying, treatment of low-concentration odors |
(2)Medium and high concentration waste gas (500 – 5000mg/m³)
| technology | Principle | Typical process | Applicable scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
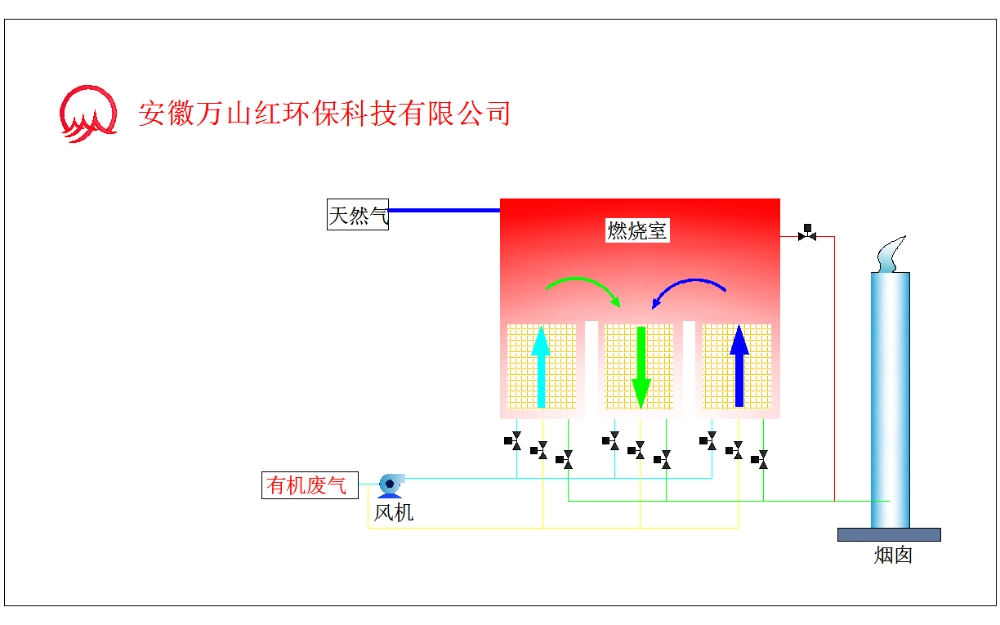
| Catalytic combustion (RCO) | Catalysts oxidize VOCs to CO₂ + H₂O at low temperatures | Activated carbon adsorption + catalytic combustion integrated machine | Printing and drying line, automotive repair painting |
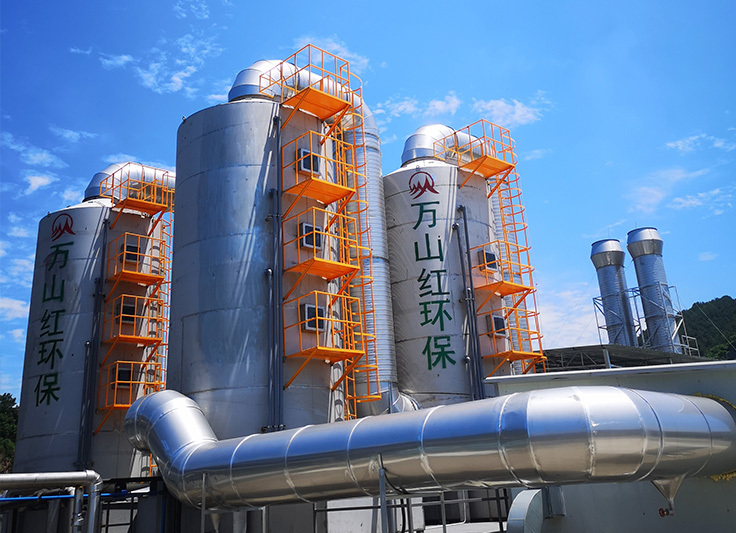
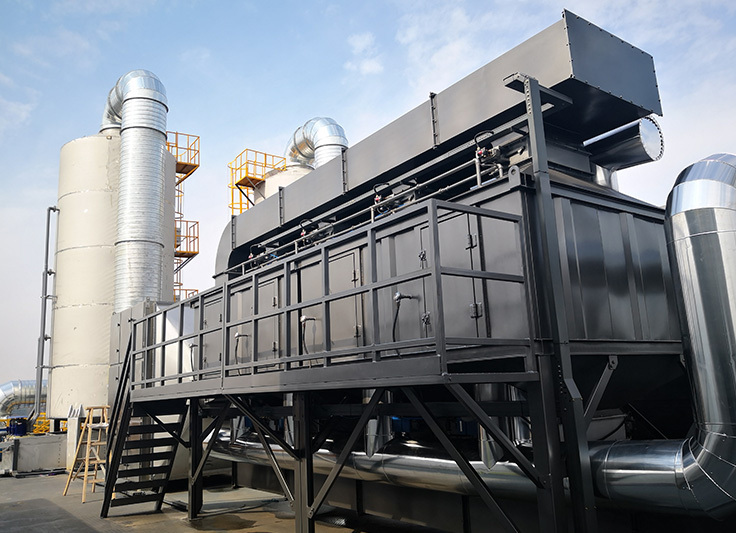
| Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) | High – temperature incineration + heat recovery of regenerator | Zeolite Rotating Wheel Concentration + RTO | Large printing enterprises (web-fed printing), container painting |
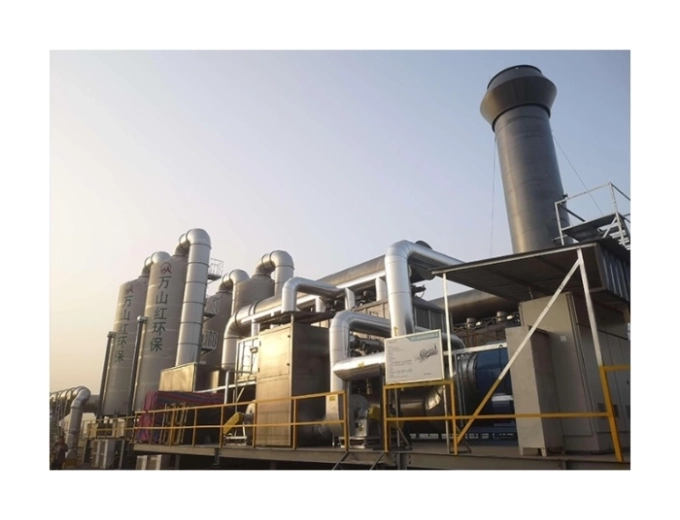
III. Typical technological processes
(1) Printing enterprises (solvent-based inks, medium scale)
Technological process:Gas collection hood (collection efficiency ≥ 90%) → Primary – effect filtration (removal of ink particles) → Activated carbon adsorption box (2 sets in rotation, off – line regeneration) → Fan → Discharge up to standard (VOCs concentration < 50mg/m³).
(2) Automobile spraying line (solvent-based paint)
Technological process:Spray booth (water swirl to remove paint mist, wastewater enters the flocculation tank) → Drying room (top air supply + side suction) → High – efficiency filter box (glass fiber wool) → RTO incinerator (temperature 800℃, residence time > 2s) → Chimney (waste heat is used to preheat fresh air).
IV. Industry Pain Points and Solutions
- Risk Control of Flammable and Explosive Substances ◦
- Measures:
- Use anti-static materials for exhaust gas pipelines, and install flame arresters and explosion relief discs;
- Configure online VOCs concentration monitoring for RTO/RCO equipment. When the concentration exceeds 25% of the lower explosive limit (LEL), automatically dilute with fresh air.
- Measures:
- The treatment cost of waste gas with low concentration and high volume is high.
- Measures:
- Adopt the zeolite rotary concentrator technology (with a concentration multiple of 10 – 20 times) to convert low – concentration waste gas into medium – high concentration, reducing the combustion energy consumption.
- Small – scale enterprises can choose activated carbon adsorption + moving bed regeneration (a third – party professional team replaces the saturated carbon regularly) to avoid building their own regeneration systems.
- Measures:
- Paint mist adhesion equipment ◦
- Measures:
- Set up multi – stage filtration (primary + medium – efficiency + high – efficiency) at the front end of the painting line, and replace the filter cotton regularly (it is recommended to replace it once every two weeks);
- Use anti – adhesion coating activated carbon or ceramic catalysts to reduce the risk of paint mist blockage.
- Measures:



.png) Inquire
Now
Inquire
Now